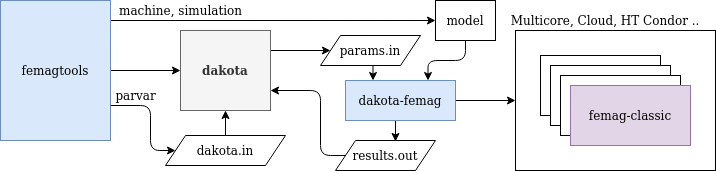
Dakota Integration¶
Dakota <https://dakota.sandia.gov>_ is an open source toolkit (GPL License) for sensitivity analysis, uncertainty quantification, model calibration and optimization developped by Sandia National Laboratories.
Note
This module is in experimental state.
Example Parameter Study with Latin Hypercube Sampling:
machine = dict(
name="PM 130",
poles=4,
...
stator=dict(
num_slots=12,
..
statorRotor3=dict(
slot_width=3e-3,
... ) ),
magnet=dict(
...
magnetSector=dict(
magn_shape=0.025,
magn_width_pct=0.8,
... ) ),
windings=dict(
num_wires=20,
.. )
)
parvar = {
decision_vars = [
{'bounds': [2e-3, 4e-3],
'name': 'stator.statorRotor3.slot_width'},
{'bounds': [0.75, 0.85],
'name': 'magnet.magnetSector.magn_width_pct'},
{'bounds': [0.021, 0.0335],
'name': 'magnet.magnetSector.magn_shape'}
],
objective_vars = [
{'name': 'dqPar.torque[-1]', 'label': 'Load Torque/Nm'},
{'name': 'torque[0].ripple', 'label': 'Cogging Torque/Nm'},
{'name': 'torque[-1].ripple', 'label': 'Torque Ripple/Nm'}
]
}
simulation = dict(
speed=5000.0 / 60,
calculationMode="pm_sym_fast",
magn_temp=20.0,
wind_temp=60,
period_frac=6,
current=28.3,
angl_i_up=0.0)
workdir = pathlib.Path.home() / 'parstudy'
workdir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
sampling = femagtools.dakota.Sampling(workdir,
magnetizingCurves=magnetizingCurve, magnets=magnetMat)
# start calculation
results = sampling(parvar, machine, simulation,
samples=100, partitions=6,
engine=dict(module='femagtools.multiproc'))
Result: dict Object with keys:
x |
array of decision (input) var values |
f |
array of objective (response) var values |
samples |
|
moments |
mean, std dev, skewness, kurtosis |
conf95 |
95% confidence intervals for each response |
corr |
correlation among all inputs and outputs |
corrpartial |
partial correlation between input and outputs |
rank |
rank correlation |
opt |
best inputs and outputs |
Example:
x = results['x']
f = results['f']
# print header
print(' '.join(['{:15}'.format(s)
for s in [d['label']
for d in parvar['decision_vars']] +
[o['label']
for o in parvard['objective_vars']]]))
print()
# print values in table format
for l in np.vstack((x, f)).T:
print(' '.join(['{:15.6f}'.format(y) for y in l]))
